Sudoku and Solver
Sudoku and Solver
Intermediate
The technique of the intermediate class is the work of filling in empty numbers with possible numbers and scrutinizing. A technique that can be said to be "the essence of Sudoku", if you understand this 100%, you can almost solve any sample other than the highly distorted samples. The samples are also complicated in the intermediate class, and usually it will take about 15 to 30 minutes to solve.
After completing the vertical and horizontal entry in the beginner class, enter the numbers that may be applicable to the intermediate class for each column or row. First of all, let's check the example which can be solved by number entry.
*Intermediate / Example 1
* Answer procedure
1.Beginner class vertical and horizontal entry

2.Number of intermediate class entry
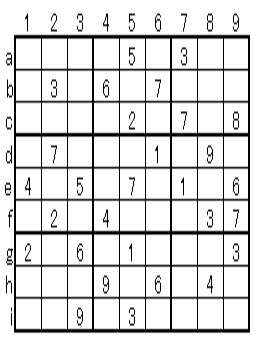
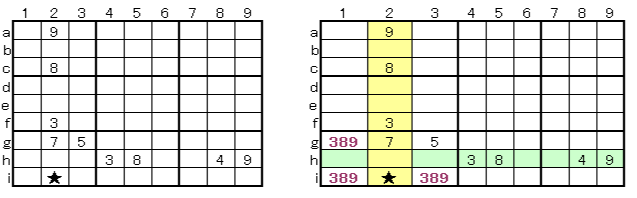
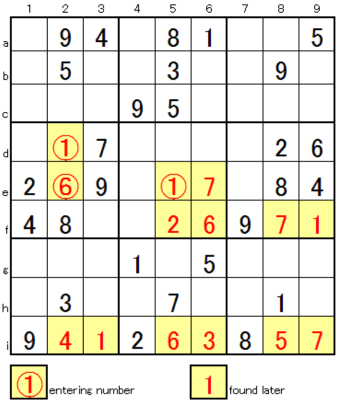
In this example, enter the possible numbers from column a to i on the horizontal line on the left, and enter the possible numbers in each cell (In this example, we scanned the horizontal column. However, scanning vertical row 1 to 9 is also OK.) The cell of A (3b) is determined to be 8 because there are 1 and 5 in row 3, with the possibility of 158 in column b. Similarly, G (2h) is determined to be 1 because column h has 137 and row 2 has 3 and 7. In these two decisions, the row 1 to 3 are determined as shown on the right. It is possible to easily lead to the solution if you get here.
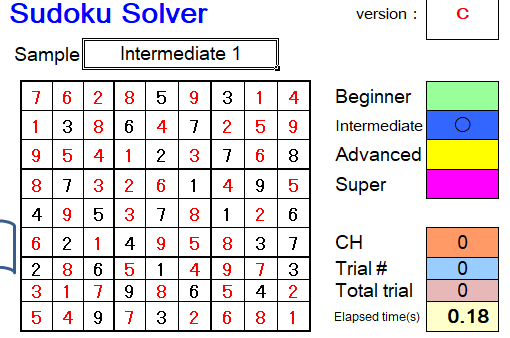
This sample can be solved instantaneously (0.18seconds) as Intermediate level in Sudoku Solver.
2. I Technique 2 (With number entry and scrutiny)
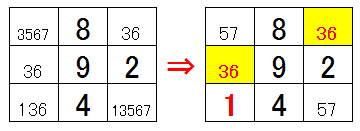
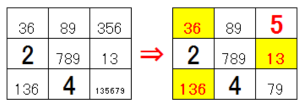
With number entry and scrutiny, scrutinize numbers in a certain area, a certain column and a certain row. In the lower case there are two 36 possible cells. If 3 is in one box, 6 is in the other box. If 6 is included, the other cells are 3. That is, since 3 and 6 are occupied by these 2 cells, 3 and 6 do not enter other cells. Therefore, the area on the left can change to the area on the right. The same is true for columns and rows that are outside the area. It is pattern A (2numbers x 2) with scrutiny.
The same is true for combinations 36-13-136, as in the example below. The number 136 is occupied by these 3 cells. It is pattern C (2 numbers X 2 numbers X 1) with scrutiny.
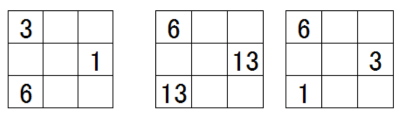
Organizing with scrutiny is as follows.
Pattern Number Decided
A: 2 numbers X 2 23, 23 23
B: 2 numbers X 3 37, 38, 78 378
C: 2 numbers X 2, 3 numbers X 1 47, 78, 478 478
D: 2 numbers X 1, 3 numbers X 2 37, 379, 379 379
E: 3 numbers X 3 234, 234, 234 234
F: 2 numbers X 2, 4 numbers X 2 45, 89, 4589, 4589 4589
3. I Technique 3 (2 cells reservation)
2 cells reservation and 3 cells reservation are applied techniques with number entry and scrutiny. Even if you do not know these applied techniques, you can get the same conclusions by entering numbers and reviewing them, but if you know them, you can answer faster. According to the 2 numbers of other area to be restricted, 2 numbers of 2 cells of the area concerned are reserved. In the case below, since the combination of 68 is in the yellow row 5 and the green column h, H (6 g) and H (6i) are decided (reserved) in 68, and only 7 is in ★. Thus, the technique to determine the cells of★ by the 2 cells reservations according to the other columns and rows even without a few scrutiny is called 2 cells reservation.
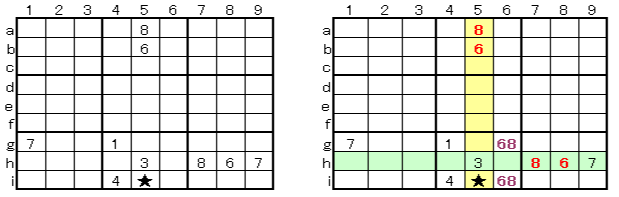 ★⇒7
★⇒7Analysis of area G of the number scrutiny in the case of not knowing this technique, with pattern E (3 numbers x 3) with scrutiny
The procedure is as follows.
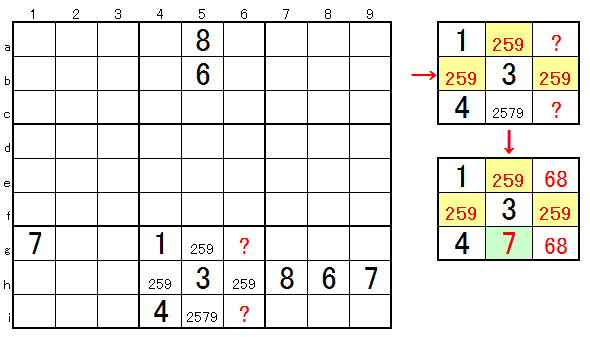
4. I Technique 4 (3 cells reservation)
In the case below, 3 cells of 3 cells of the area concerned are reserved according to 3 figures of the other area to be constrained. It will be done. Therefore, only 4 is in ★. A technique that takes advantage of the fact that 3 cells are reserved by other columns and rows in this way is called 3 cells reservation.
 ★⇒4
★⇒4If you do not know this technique, analysis of area G of number scrutiny will be the following procedure.
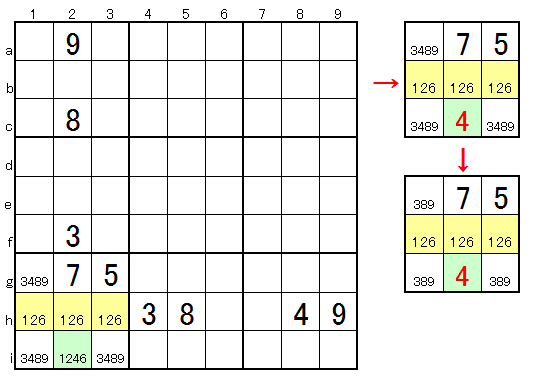
★ G (2i) is determined to be 4 in the pattern E (3 numbers X 3) 126 with scrutiny.
*Intermediate / Example 2
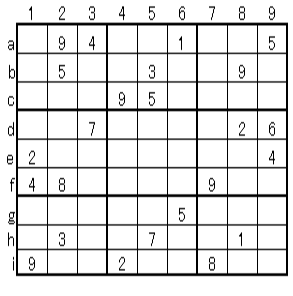
* Answer procedure
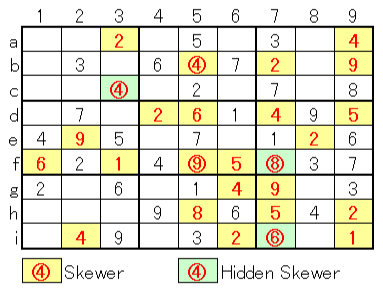
1. Beginner class: Fill in the vertical and horizontal lines + skewer
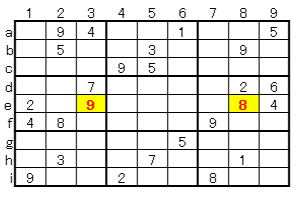
2. Intermediate class: cells to be found without entering numbers and scrutiny
3. With number entry and scrutiny
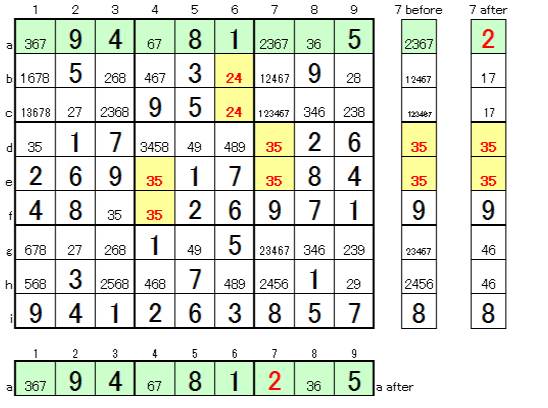
* Possibility of 2 in column a is only C (7a), so C (7a) is decided as 2
* As there are 35-35 combinations in row 7, it changes as shown on the right with the decision of 2.
(35-35 in row 4, 24-24 in row 6 also change the corresponding cells)
⇒ Then, other cells are determined.
4. Further scrutiny
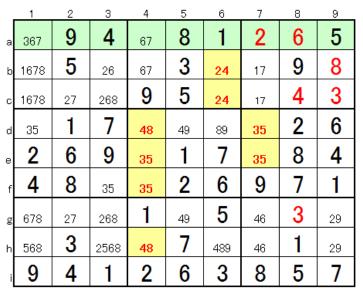
↑ It's easy if you get here
This example took 0.23 seconds as intermediate level in the Sudoku Solver.
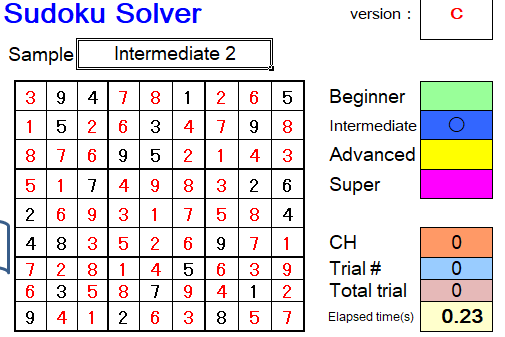
If you understand this, please proceed to the advanced class next !